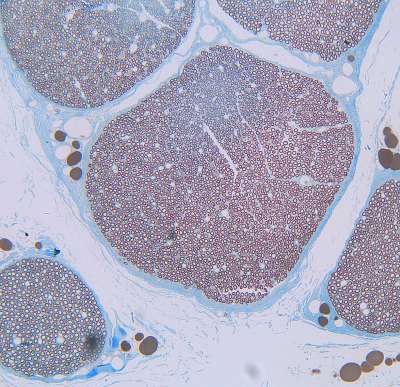
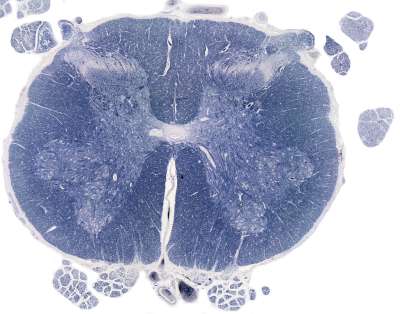
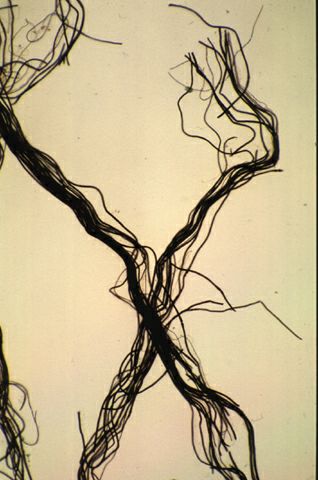
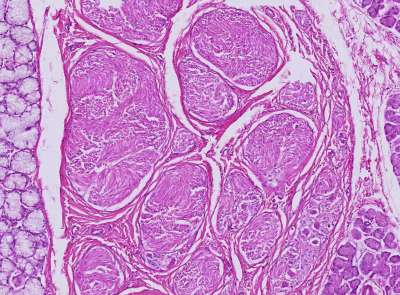
Course 7 - Nervous tissue
There are many ways to classify nervous tissue.
Anatomically, it is divided into the
- peripheral nervous system (PNS) and the
- central nervous system (CNS).
Functionally, it can be divided into a
- somatic part, which handles voluntary movements, and an
- autonomic part, which handles involuntary movements and glandular secretions.
In histology, we do not focus on location or function, but instead look at cell types and categorize them into
- neurons and
- glial cells.
Neurons have a large cell body, and due to the high activity in these cells, they must constantly produce new enzymes and other proteins. This requires a lot of extended chromatin in the nucleus, which contributes to the characteristic appearance of the neuron. The neuron has a varying number of extensions. Most of these extensions are dendrites, which receive signals from other neurons. The neuron transmits the signal further via a single extension, the axon.